Install Kubernetes Cluster on Ubuntu server 22.04
This guide will walk you through setting up a Kubernetes cluster with one master node and two worker nodes using Ubuntu Server 22.04.
Prerequisites
- Three VMs running Ubuntu Server 22.04
- Network connectivity between all nodes
In this guide, I’m using VMware with NAT networking. Here are my node IP addresses:
- k8s-master: 192.168.72.129
- k8s-worker1: 192.168.72.130
- k8s-worker2: 192.168.72.131
You can find your IP addresses by running
ip ain each VM.
Step 1: Preparation
Preparing the Environment
First, update all packages on each node:
1
2
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
Reboot to apply any kernel updates:
1
sudo reboot
Set up the hostnames for each node:
On the master node:
1
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname "k8s-master.quocanuit.local"
On worker1:
1
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname "k8s-worker1.quocanuit.local"
On worker2:
1
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname "k8s-worker2.quocanuit.local"
Modifying /etc/hosts on All Nodes
Edit the hosts file on each node:
1
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Add the following entries:
1
2
3
192.168.72.129 k8s-master.quocanuit.local k8s-master
192.168.72.130 k8s-worker1.quocanuit.local k8s-worker1
192.168.72.131 k8s-worker2.quocanuit.local k8s-worker2
Disabling Swap
Kubernetes requires swap to be disabled. On all nodes:
1
sudo swapoff -a
Verify that swap is disabled:
1
free -h
To make this change permanent, edit /etc/fstab:
1
sudo nano /etc/fstab
Comment out the swap line:
Apply the changes:
1
sudo mount -a
Configuring Kernel Settings
Load the necessary kernel modules:
1
2
3
4
sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/containerd.conf <<EOF
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
Activate the modules:
1
2
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
Set kernel parameters for Kubernetes:
1
2
3
4
5
sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf <<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
Apply the changes:
1
sudo sysctl --system
Step 2: Installing Containerd
Install containerd and its dependencies:
1
2
3
4
5
sudo apt install -y curl gnupg2 software-properties-common apt-transport-https ca-certificates
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmour -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/docker.gpg
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y containerd.io
Configure containerd:
1
2
3
4
containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml >/dev/null 2>&1
sudo sed -i 's/SystemdCgroup \= false/SystemdCgroup \= true/g' /etc/containerd/config.toml
sudo systemctl restart containerd
sudo systemctl enable containerd
Step 3: Installing Kubernetes Components
Add the Kubernetes repository:
1
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Add the Kubernetes repository:
1
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/ /" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
1
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
Install Kubernetes components:
1
2
3
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Step 4: Initializing the Cluster
On the master node only:
1
2
3
sudo kubeadm init \
--pod-network-cidr=10.10.0.0/16 \
--control-plane-endpoint=k8s-master.quocanuit.local
After initialization, set up kubectl:
1
2
3
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Verify the cluster status:
1
2
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodes
Joining Worker Nodes
On worker nodes, use the join command output from the master’s initialization. If needed, regenerate the join command on the master:
1
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
Step 5: Installing Calico Network Plugin
On the master node, download and install Calico:
1
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.25.0/manifests/calico.yaml -O
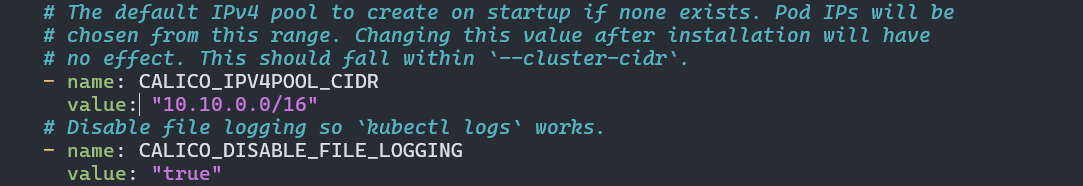
Modify the CIDR in the Calico config:
1
sudo nano calico.yaml
Update the CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR to match your pod network CIDR:
Apply the configuration:
1
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
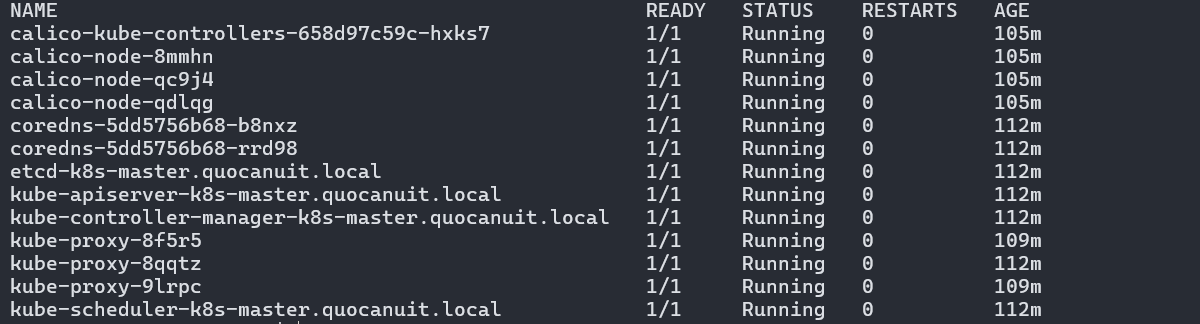
Verify the installation:
1
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
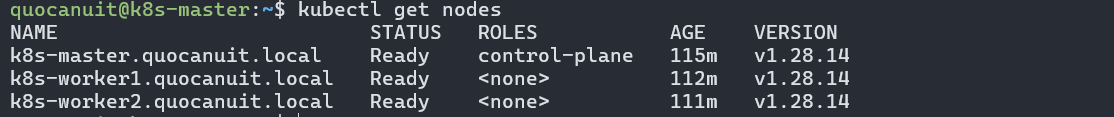
Check node status:
1
kubectl get nodes
Step 6 (optional): Installing Kubernetes Dashboard
For better cluster management, install the Kubernetes Dashboard:
1
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.7.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
Create a file named kubernetes-dashboard-service-np.yaml:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard-service-np
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8443
nodePort: 30002
targetPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
Apply the configuration:
1
kubectl apply -f kubernetes-dashboard-service-np.yaml
Generate an authentication token:
1
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard create token admin-user
Access the dashboard at https://192.168.72.129:30002 and enter the token.
If you can’t access the dashboard, verify your IP and port settings. You might need to set up SSH tunneling for secure access.
After successful login, you’ll see the Kubernetes Dashboard: